The Reverse DNS (rDNS) lookup is a process that converts an IP address back to its associated domain name. Typically:
A standard DNS translates a domain name (e.g., gmail.com) into its IP address.
An rDNS does the opposite: it translates an IP address back to its domain, revealing where the email is originating from.
This process is crucial because email providers, like Gmail, check the rDNS of the sender to assess the legitimacy of the sending domain.
The IP address and rDNS are critical for determining:
If your emails are coming from a trusted infrastructure.
Whether the originating IP is associated with spam or other negative indicators.
Although a blacklisted Gmail IP might show up in this section, it usually does not impact deliverability significantly due to the nature of rotating Gmail IPs.
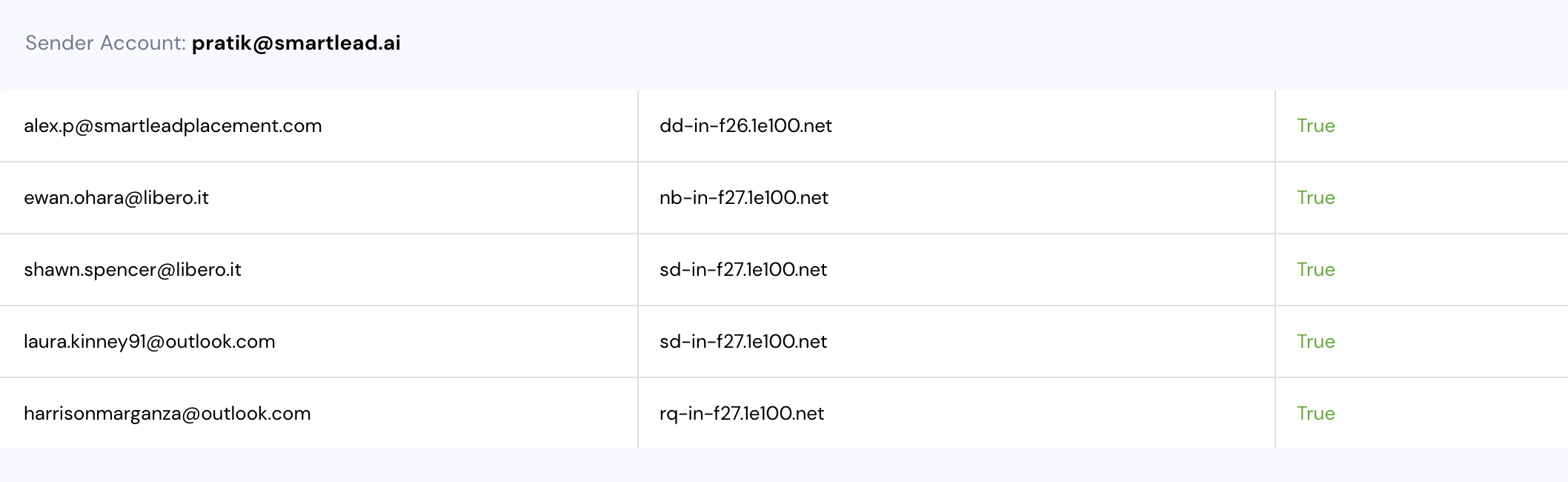
Most of Google's network resolves to the domain 1e100.net. When emails are sent from Gmail, they originate from this domain, not from SmartLead's sending infrastructure. Here’s how it works:
IP Address ↔️ Domain Name (1e100.net) ↔️ Gmail's Network
If you see an rDNS resolving to 1e100.net, it indicates the email originated from a Gmail IP address. This is expected behavior and confirms that the Gmail infrastructure is sending your emails.
You may notice discrepancies in the rDNS data, which can be due to:
DNS Resolution Timing: The point in time when the DNS query was made can affect the result.
Network Caching: DNS data may be cached differently across servers, causing slight variations.
IP Origin Dynamics: Google’s network includes many IPs, and their resolution paths can vary, but they all point back to Google's domain 1e100.net.